How do consumers choose from the many types and specifications of wires?
Nowadays, every household has electricity. Fires caused by overloaded wires are not uncommon every year, such as short circuit, overload, leakage, poor contact and other factors. The laying of wires is an invisible installation that cannot be touched or seen in the field of decoration. It is like the blood vessels of the human body, a channel connecting various links and a lifeline. When you return home, turn on the lights, turn on the TV, and listen to music, you may be able to truly enjoy the comfort of home. The safe use of electricity in every household can be regarded as a thousand lights.
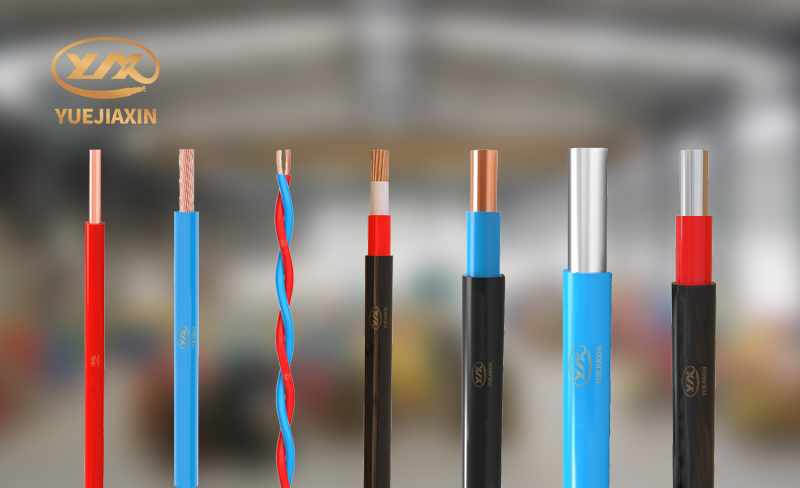
Therefore, choosing a wire that is of good quality, durable, suitable for oneself and economical has become the first choice for many consumers to decorate. When choosing wires at first, many people faced the same problem: there are too many types of wires, and each type has different specifications. How to choose?
1. Types of wires
In fact, to choose what wires, you must first look at what types are available. The types of wires include insulated wires, flame-retardant wires, halogen-free low-smoke wires, etc. Commonly used ones are polyvinyl chloride insulated wires, polyvinyl chloride insulated soft wires, etc.
Usually we call the wires with only insulation layers "wires", and those with not only insulation layers but also sheath layers are called "cables". Common wire and cable models include: BV, BVR, RV, RVV, RVS, etc.
You can choose BV or BVR in home decoration. BV wire is a single-strand wire with only one thicker copper conductor in the insulation layer. It is relatively hard, but its overload capacity and weather resistance are much better than BVR. BVR is a multi-strand wire with multiple thinner copper conductors in the insulation layer. Compared with BV wire, it is softer, has a stronger current capacity, is more convenient to construct, and is more expensive.
Since BV wire is a single-strand wire, compared with BVR of the same cross-sectional area, its copper wire is thicker and not easy to burn out when the temperature is high for a long time. The copper wire of BVR wire is relatively thin, and it is easy to burn out one or two of them when the temperature is high. As long as one or two copper wires in the wire are burned out, the burned cross-sectional area is reduced, the resistance is greater, and the wire is more likely to be burned.
In practical applications, since BVR wire is relatively soft, the joints are easy to loosen over time. BV wire is relatively much better, so in home decoration, in order to prevent the joints from loosening, the "tinning" process must be adopted.
2. The cross-section of the wire
When consumers buy wires, they are generally asked by merchants how many square meters of wire they want to buy. Note that the square meters here do not refer to the number of wires, but specifically refer to the cross-sectional area of each (coil) wire (mm). The larger the square, the thicker the conductor (copper wire).
For example, BV wires generally have multiple specifications for household use, such as 1.5 square meters, 2.5 square meters, 4 square meters, 6 square meters, and 10 square meters. Consumers should calculate which specification to buy and the purchase quantity based on the use of electrical appliances at home. So, how to determine which specification to buy? This requires calculating the rated current based on the load of household appliances, thereby determining the cross-sectional area of the wire and ultimately determining the specifications of the wire.
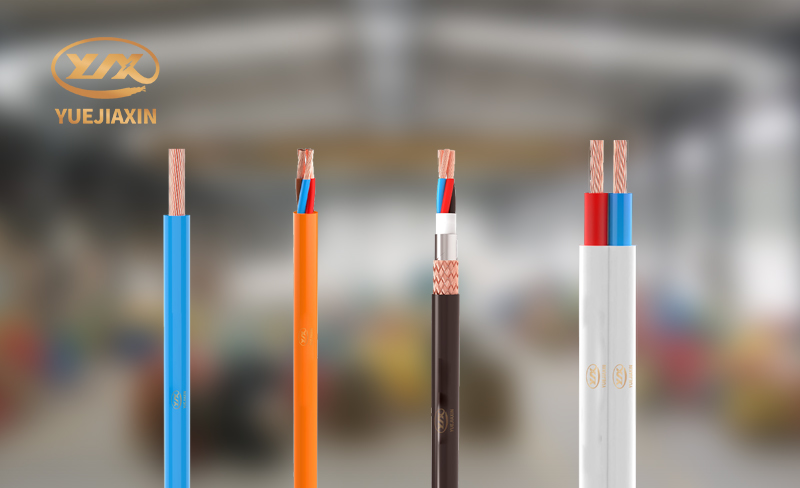
In the actual process of purchasing wires, we must choose suitable wire products based on our actual usage and usage scenarios.




