What is shielded cable?
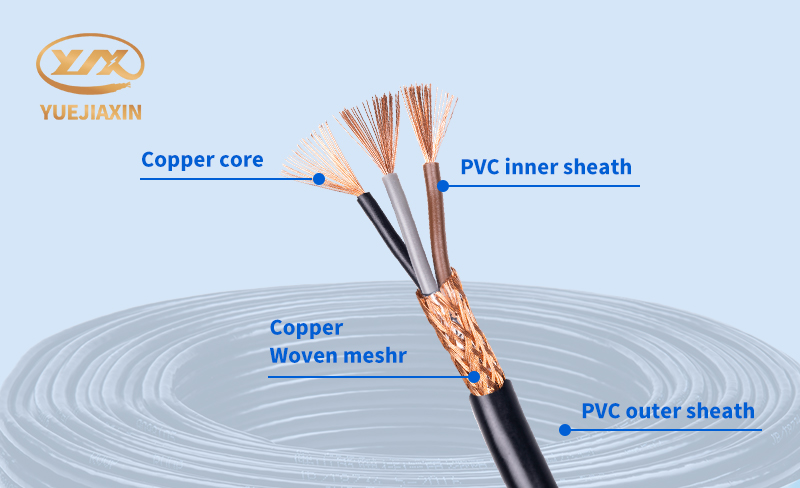
Shielded cable, as its name suggests, is different from others. It is like putting on a layer of "protective clothing" for the signal transmission line. It is a transmission line that uses a metal mesh braided layer to wrap the signal line. The braided layer is generally red copper or tinned copper. Of course, the material of the shielding layer is not limited to this. Metal foil, metal tube, etc. are also common. Shielding layers of different materials will vary in shielding effect and application scenarios. Structurally, shielded cables are mainly composed of four parts: inner conductor, insulation layer, shielding layer and outer sheath.
The inner conductor is the core, just like the main road of a highway, where current or signal runs at high speed. It is usually made of highly conductive metals such as copper or aluminum. According to different usage requirements, the inner conductor can be a single solid wire or a multi-strand twisted wire. The insulation layer is like a barrier on both sides of the road, isolating the inner conductor from the outside world, preventing current leakage, and ensuring the safety of transmission. Common insulating materials include polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, cross-linked polyethylene, etc. These materials have good electrical insulation properties, mechanical properties and chemical stability.
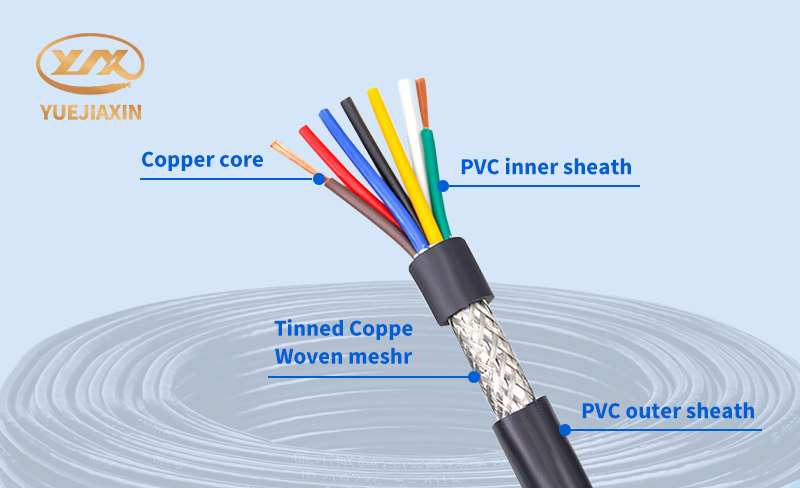
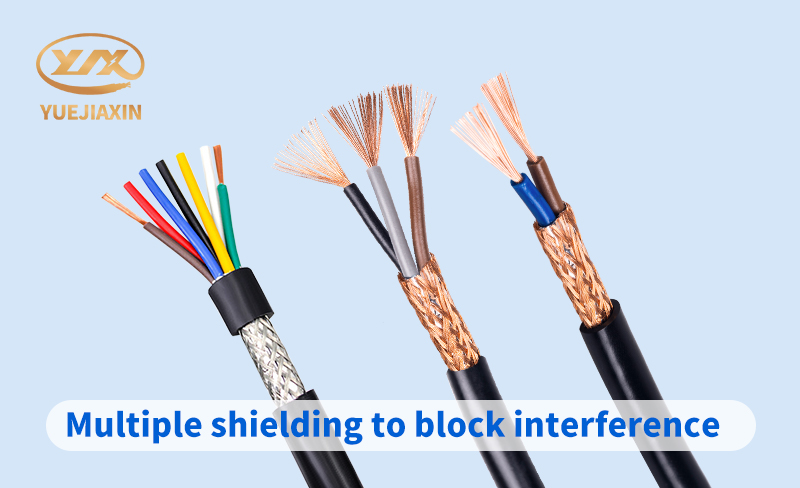
The shielding layer is the key to shielded cable. It is like an "electromagnetic guard" responsible for blocking external electromagnetic interference from entering the cable, while preventing the signal transmitted inside the cable from leaking out, avoiding interference with other surrounding devices. The shielding layer can be in the form of metal foil, braided mesh or metal tube. Different shielding structures have their own advantages and disadvantages in shielding effect. The braided mesh shielding layer has good flexibility, which is convenient for bending and installing cables. It is widely used in some occasions where cables need to be moved or bent frequently; the metal foil shielding layer has a good shielding effect on low-frequency interference. The outer sheath is the outermost layer of the cable, which is equivalent to a solid "armor". Its main function is to protect the internal structure of the cable from mechanical damage, chemical corrosion and environmental factors, and to extend the service life of the cable. Common outer sheath materials include polyvinyl chloride, polyethylene, rubber, etc. These materials have good wear resistance, corrosion resistance and mechanical strength.
Shielded cables can effectively resist electromagnetic interference. Their working principle is mainly based on the unique way the shielding layer acts on electromagnetic waves, namely reflection, absorption and skin effect. When the external electromagnetic interference wave "attacks", the shielding layer is like a solid "shield", and most of the interference waves will be directly reflected back, making it impossible for them to enter the cable to interfere with signal transmission.
Proper use and maintenance of shielded cables can give full play to their performance advantages, extend their service life, and ensure the stable operation of equipment and systems. Here are some practical methods and key points.
When choosing shielded cables, you should fully consider the actual needs and application environment. You should also pay attention to the specifications of the cable, and select the appropriate conductor cross-sectional area, shielding layer structure and insulation material according to factors such as the type, frequency, power and transmission distance of the transmitted signal. When installing shielded cables, you must strictly follow the relevant specifications and standards. During use, you should also regularly inspect and maintain the shielded cables.
With the continuous advancement of science and technology, shielded cables are also constantly developing and innovating. In the future, it will achieve greater breakthroughs in performance improvement, material innovation, structural optimization and application expansion, providing strong support for the development of more emerging technologies.




