Do you know how wires and cables are made?
The manufacturing of wires and cables is completely different from the production of most electromechanical products. Electromechanical products usually use parts to assemble into components, and then assemble multiple components into a single product, and the product is measured by the number of units or pieces. Wires and cables are measured by length. All wires and cables start with conductor processing, and insulation, shielding, cabling, sheathing, etc. are added layer by layer on the outside of the conductor to make wire and cable products. The more complex the product structure, the more layers are superimposed.
1. Copper and aluminum monofilament drawing
The copper and aluminum rods commonly used in wires and cables are made of one or more drawing dies at room temperature by a wire drawing machine to reduce their cross-section, increase their length, and improve their strength. Wire drawing is the first process of each wire and cable company, and the main process parameter of wire drawing is die matching technology.
2. Monofilament annealing
When copper and aluminum monofilaments are heated to a certain temperature, they are recrystallized to increase the toughness of the monofilaments and reduce their strength to meet the requirements of wires and cables for conductive cores. The key to the annealing process is to prevent the oxidation of copper wires.
3. Conductor twisting
In order to improve the softness of wires and cables and facilitate laying and installation, the conductive core is made of multiple monofilaments twisted together. From the twisting form of the conductive core, it can be divided into regular twisting and irregular twisting. Irregular twisting is further divided into bundle twisting, concentric twisting, special twisting, etc. In order to reduce the area occupied by the conductor and reduce the geometric size of the cable, the conductor is twisted and compressed at the same time, so that the ordinary round shape is transformed into a semicircle, fan-shaped, tile-shaped and compressed round shape. This kind of conductor is mainly used in power cables.
4. Insulation extrusion
Plastic wires and cables mainly use extruded solid insulation layer. The main technical requirements for plastic insulation extrusion are: eccentricity, smoothness, density
5. Cabling
For multi-core cables, in order to ensure the molding degree and reduce the shape of the cable, it is generally necessary to twist them into a circle. The twisting mechanism is similar to the conductor twisting. Due to the large twisting section diameter, most of them adopt the non-back-twist method. The technical requirements for cabling are: first, to prevent the twisting of the cable caused by the turning over of the special-shaped insulation core; second, to prevent the insulation layer from being scratched. Most cables are accompanied by the completion of two other processes during cabling: one is filling, to ensure the roundness and stability of the cable after cabling; the other is binding, to ensure that the cable core is not loose.
6. Inner sheath
In order to protect the insulating core from being damaged by the armor, the insulation layer needs to be properly protected. The inner sheath is divided into: extruded inner sheath (isolation sleeve) and wrapped inner sheath (cushion). The wrapped cushion replaces the binding tape and is carried out simultaneously with the cabling process.
7. Armor
The cables laid underground may be subjected to a certain positive pressure during operation, and the inner steel belt armor structure can be selected. The cable is laid in places with both positive pressure and tension (such as water, vertical shafts or soil with a large drop), and the structure with inner steel wire armor should be selected.
8. Outer sheath
The outer sheath is a structural part that protects the insulation layer of wires and cables from erosion by environmental factors. The main function of the outer sheath is to improve the mechanical strength of wires and cables, resist chemical corrosion, moisture, and prevent cable combustion. According to different requirements for cables, the plastic sheath is directly extruded using an extruder.
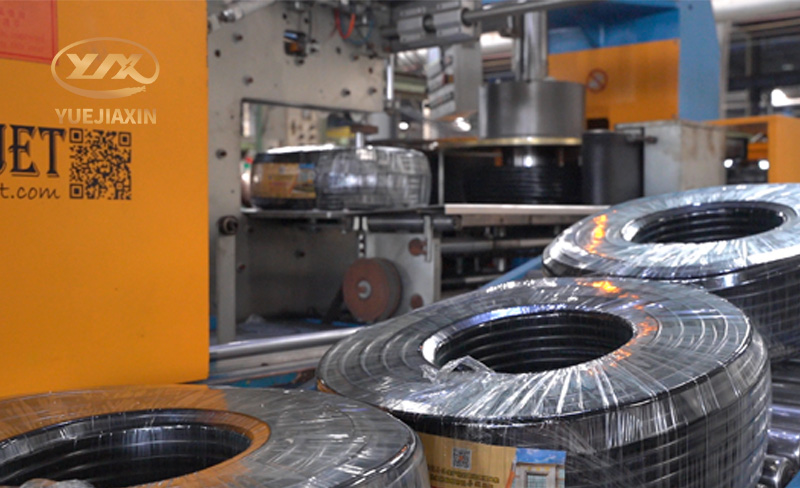

From the production stage to the hands of consumers, wires and cables go through multiple processes. The more complex the specifications of wires and cables, the higher the repeatability.




